RESTAURATEURS! FINI LES LOYERS ABUSIFS!



VOTRE SOLUTION !
Kitchen Six, votre solution innovante dans le domaine des "food halls". Nous offrons une approche moderne et flexible pour les restaurateurs qui souhaitent s'adapter aux évolutions du marché. Notre concept vous permet de bénéficier d'une indépendance accrue, tout en réduisant significativement vos dépenses.
Kitchen Six est un espace partagé où plusieurs restaurateurs peuvent cuisiner et vendre leurs plats sans avoir besoin d'un restaurant traditionnel. Cela leur permet de réduire les coûts, d'être plus flexibles et de se concentrer sur la qualité de leur nourriture. Les clients peuvent commander une variété de plats en un seul endroit, ce qui rend l'expérience de repas plus pratique et agréable.
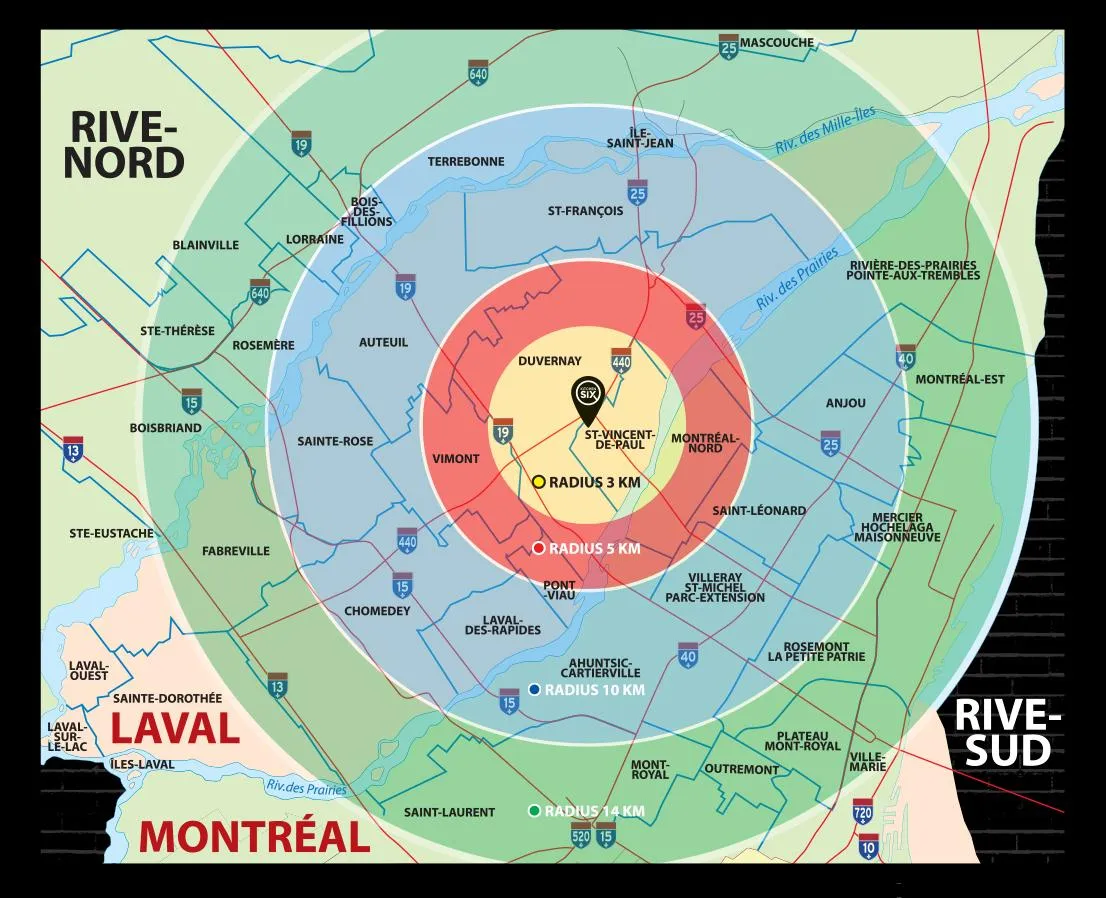
SALLE DISPONIBLE SUR PLACE !

PARTENAIRES
Avec qui nous collaborons









